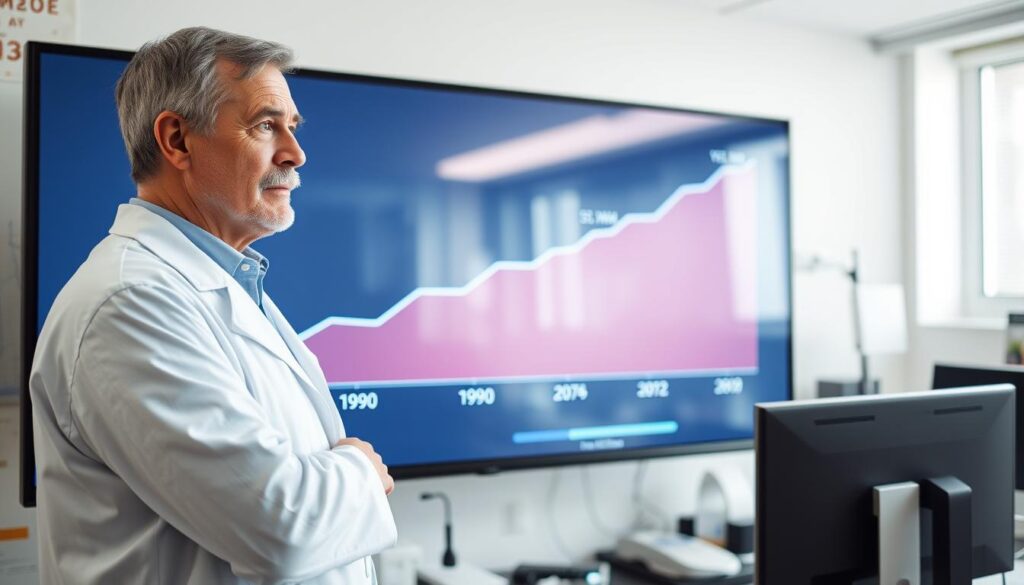
Projected Diabetes Prevalence in the US: What Percentage of Americans Will Be Affected?
Did you know that diabetes rates have doubled in the US since 1990? This chronic disease affects millions, with 14% of adults living with it in 2022. Globally, the numbers are staggering, reaching 830 million people. Diabetes impacts your body and blood sugar levels, making early treatment essential.
Understanding the trends and factors behind this rise is crucial. From lifestyle changes to insulin management, the fight against diabetes requires awareness and action. Let’s explore the statistics, projections, and what they mean for the future.
Key Takeaways
- Diabetes rates in the US have doubled since 1990.
- Globally, 830 million people are affected by this disease.
- Early treatment is vital for managing diabetes effectively.
- Lifestyle changes play a significant role in prevention.
- Understanding trends helps in creating better health strategies.
Table of Contents
Introduction: Understanding Diabetes in the United States
Diabetes has become a growing concern in the US, affecting millions annually. This chronic disease occurs when your body struggles to produce or use insulin effectively. Over time, it can lead to serious health complications if not managed properly.
Overview of Diabetes as a Chronic Disease
Diabetes is classified as a noncommunicable disease, meaning it’s not contagious but develops over time. It’s primarily categorized into two types: type 1 and type 2. Type 1 is an autoimmune condition, while type 2 is often linked to lifestyle factors.
Historically, diabetes was considered rare. However, modern lifestyles and dietary changes have contributed to its rise. Today, it’s one of the leading causes of health issues among adults.
Your Role in Recognizing Its Impact
Understanding diabetes starts with recognizing its symptoms. High blood sugar levels, frequent urination, and fatigue are common signs. Early detection can make a significant difference in managing the disease.
Your awareness and proactive steps can help reduce its impact. Regular check-ups, a balanced diet, and physical activity are essential for prevention and management.
| Key Facts About Diabetes | Statistics |
|---|---|
| Adults with diabetes in the US | 38.1 million (14.7%) |
| Undiagnosed cases | 8.7 million |
| Adults with prediabetes | 97.6 million (38%) |
Diabetes is more than just a health issue; it’s a societal challenge. By staying informed and taking action, you can play a vital role in combating this disease.
Diabetes Prevalence: Historical Trends and Future Projections
Since 1990, diabetes has transformed from a rare condition to a widespread epidemic. The number of people affected globally skyrocketed from 200 million to over 830 million by 2022. This noncommunicable disease has become a significant health challenge, especially in the US.
Change in Rates Since 1990
In the US, diabetes rates have more than doubled over the past three decades. From 5.5 million cases in 1980, the number surged to 38.1 million by 2022. This rise is attributed to lifestyle changes, increased obesity rates, and aging populations.
Globally, the trend is similar. Countries with high-income levels saw steady increases, while low- to middle-income nations experienced even sharper rises. This highlights the global nature of the diabetes epidemic.
Future Forecasts and Statistical Models
Projections suggest that diabetes prevalence will continue to climb. By 2060, over 60 million adults in the US could be living with this condition. Statistical models predict an annual increase of 0.3% in prevalence rates until 2030.
Globally, the numbers are even more alarming. Estimates indicate that over 1.3 billion people could be affected by 2050. This underscores the urgent need for preventive measures and better management strategies.
Impact of Socioeconomic Factors
Socioeconomic factors play a crucial role in diabetes prevalence. Lower income levels and limited access to healthcare contribute to higher rates in underserved communities. Education and awareness also influence prevention and management.
For example, in the US, black adults have a higher prevalence compared to other groups. This disparity highlights the need for targeted interventions to address inequities in healthcare access and outcomes.
Understanding these trends and projections is essential for shaping effective health policies. By addressing both medical and socioeconomic factors, we can work towards reducing the burden of diabetes globally.
Global Diabetes Trends and Their US Comparisons
Global diabetes trends reveal stark contrasts between high-income and low- to middle-income countries. While the US has seen a steady rise in cases, the increase in low- to middle-income regions is even more alarming. Understanding these disparities is crucial for shaping effective healthcare strategies.
Differences Between High-Income and Low- to Middle-Income Countries
In high-income countries, diabetes prevalence has stabilized or declined in recent years. However, low- to middle-income nations face a rapid surge in cases. For example, Africa and South-East Asia report over half of their diabetes cases as undiagnosed.
This disparity is driven by limited access to healthcare, education, and resources. In contrast, high-income regions benefit from advanced medical infrastructure and awareness campaigns.
Key factors contributing to these differences include:
- Socioeconomic challenges: Poverty and lack of healthcare access in low- to middle-income countries.
- Urbanization: Rapid urban growth in these regions often leads to unhealthy lifestyle changes.
- Global initiatives: Programs like the Global Diabetes Compact aim to address these gaps.
For instance, the WHO reports that 90% of untreated diabetes cases occur in low- to middle-income countries. This highlights the urgent need for targeted interventions.
Comparing these trends with the US, where diabetes rates are high but relatively stable, underscores the importance of global cooperation. By learning from successful strategies in high-income countries, low- to middle-income nations can improve their healthcare outcomes.
Understanding these global trends is essential for shaping future US policies. It also emphasizes the need for initiatives that address both medical and socioeconomic factors in diabetes management.
Analyzing what percentage of the popultion is expected to have diabetes
Predicting diabetes prevalence involves advanced research and data analysis. Scientists use statistical models and population surveys to estimate future trends. These projections help shape healthcare strategies and resource allocation.
Methodologies Behind the Projections
Researchers rely on multiple data sources to forecast diabetes rates. Population surveys collect information on lifestyle, diet, and health conditions. Blood tests measure glucose and sugar levels, providing critical insights into diabetes risk.
Longitudinal studies track individuals over time, identifying patterns and risk factors. Yearly data updates ensure projections remain accurate and relevant. These methods combine to create reliable forecasts for future diabetes prevalence.
Interpreting Statistical Data for Your Understanding
Understanding diabetes projections can seem complex, but breaking it down helps. Blood glucose levels are a key indicator, showing how well your body manages sugar. High levels often signal diabetes or prediabetes.
Control methods like diet, exercise, and medication play a vital role in managing the condition. Statistical models incorporate this data to predict outcomes. By staying informed, you can better understand the factors influencing diabetes trends.
| Key Elements in Diabetes Projections | Details |
|---|---|
| Population Surveys | Collect data on lifestyle and health conditions |
| Blood Glucose Tests | Measure sugar levels to assess diabetes risk |
| Longitudinal Studies | Track individuals over time for patterns |
| Control Methods | Include diet, exercise, and medication |
These methodologies ensure accurate and actionable projections. By understanding the science behind the data, you can better grasp the future of diabetes prevalence.
Factors Contributing to the Rise of Diabetes
The rise in diabetes cases is driven by a mix of lifestyle and environmental factors. Understanding these contributors is essential for effective prevention and management. From poor diets to limited healthcare access, multiple elements play a role in this growing epidemic.
Lifestyle and Dietary Influences
Your daily habits significantly impact your risk of developing diabetes. A diet high in processed foods and sugary drinks can lead to raised blood sugar levels. Physical inactivity further compounds the problem, increasing the likelihood of obesity—a major risk factor.
Studies show that over 73% of adults with diabetes are overweight or obese. This highlights the importance of maintaining a balanced diet and regular exercise. Small changes, like reducing sugar intake and increasing activity, can make a big difference.
Economic and Environmental Considerations
Socioeconomic challenges also play a critical role. In low- to middle-income communities, limited access to healthcare and education exacerbates the problem. People in these areas often face barriers to proper diagnosis and treatment.
Environmental factors, such as food deserts and lack of safe spaces for physical activity, further increase the risk. For example, urban areas with limited access to fresh produce often see higher diabetes rates. Addressing these issues requires a combination of policy changes and community support.
“The diabetes epidemic is not just a medical issue—it’s a societal challenge that demands comprehensive solutions.”
| Key Contributors to Diabetes | Impact |
|---|---|
| Poor Diet | Increases blood sugar levels |
| Physical Inactivity | Raises obesity risk |
| Low-Income Status | Limits access to healthcare |
| Urban Food Deserts | Reduces access to healthy food |
By addressing these factors, you can take proactive steps to reduce your risk. Whether it’s improving your diet or advocating for better healthcare access, every effort counts in the fight against diabetes.
Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes: Impact and Differences
Diabetes comes in two main forms, each with distinct causes and treatments. While both affect your blood sugar levels, they require different approaches to care and management. Understanding these differences is key to addressing the challenges they pose.

Characteristics and Prevalence of Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where your body attacks insulin-producing cells. This means people with this type need daily insulin injections to survive. It’s less common, affecting about 8% of those living with diabetes.
This type often develops in younger individuals, with many diagnosed before age 40. Unlike type 2, it’s not linked to lifestyle factors. Currently, there’s no cure, but advancements in treatment are improving quality of life for those affected.
Understanding the Growing Epidemic of Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes makes up over 90% of all cases. It occurs when your body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough. Lifestyle factors like poor diet and inactivity significantly increase your risk.
Adults over 40 are more likely to develop type 2, especially if they’re overweight or have a family history. Unlike type 1, it can sometimes be managed or even put into remission through weight loss and lifestyle changes.
| Key Differences Between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes | Details |
|---|---|
| Cause | Autoimmune (Type 1) vs. Lifestyle/Genetics (Type 2) |
| Treatment | Insulin required (Type 1) vs. Lifestyle changes/Medication (Type 2) |
| Prevalence | 8% (Type 1) vs. 90% (Type 2) |
Both types can lead to serious complications like blood vessel damage, kidney issues, and even death if not managed properly. Early diagnosis and proper care are essential for reducing these risks.
Prevention and Early Diagnosis Strategies
Taking proactive steps today can significantly reduce your risk of developing diabetes tomorrow. By focusing on prevention and early diagnosis, you can lower the chances of complications like kidney damage and blood vessel issues. Simple lifestyle changes and regular health check-ups are your best tools in this fight.
Practical Lifestyle Modifications
Your daily habits play a crucial role in preventing diabetes. Start by adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Avoid processed foods and sugary drinks, which can spike your blood sugar levels.
Regular physical activity is equally important. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly. Even small changes, like taking the stairs or walking more, can make a big difference. These steps not only reduce your risk but also improve overall health.
The Importance of Regular Health Screenings
Early diagnosis is key to managing diabetes effectively. Regular screenings, including blood glucose tests, can detect the condition before it progresses. This allows for timely treatment and reduces the likelihood of severe complications.
If you’re over 45 or have risk factors like obesity, screenings are especially important. Early detection can prevent or delay the onset of diabetes, giving you more control over your health.
| Key Strategies for Diabetes Prevention | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Healthy Diet | Maintains stable blood sugar levels |
| Regular Exercise | Reduces obesity and improves insulin sensitivity |
| Health Screenings | Enables early diagnosis and care |
By incorporating these strategies into your life, you can take charge of your health. Prevention and early diagnosis are the most effective way to combat diabetes and its complications.
Treatment Approaches and Managing Complications
Effective diabetes treatment is essential for managing long-term health risks. Whether you’re living with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, understanding your options can help you maintain better control over your condition. From medication to lifestyle adjustments, modern approaches focus on stabilizing blood sugar levels and preventing complications.

Medication Options and Insulin Therapy
For those with type 1 diabetes, insulin therapy is mandatory. This involves daily injections or using an insulin pump to regulate blood glucose levels. Without insulin, your body cannot process sugar effectively, leading to severe complications.
Type 2 diabetes often requires a combination of treatments. Medications like metformin and SGLT-2 inhibitors help lower blood sugar and improve insulin sensitivity. These drugs are particularly effective when paired with lifestyle changes, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise.
Managing Long-term Health Risks
Diabetes increases your risk of complications like heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve issues. Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is crucial for early detection and management. For example, maintaining an A1C level below 7% can significantly reduce the likelihood of these problems.
Cardiovascular health is a major concern for adults with diabetes. Medications like statins and blood pressure drugs are often prescribed to lower raised blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Additionally, annual kidney function tests can help detect issues early, allowing for timely intervention.
“Proper diabetes management isn’t just about medication—it’s about creating a balanced approach to health.”
| Key Treatment Strategies | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Insulin Therapy | Essential for type 1 diabetes, regulates blood sugar |
| Metformin | Lowers blood glucose, improves insulin sensitivity |
| Regular Monitoring | Helps prevent complications like kidney damage |
By understanding your type diabete need, you can work with your healthcare provider to create a personalized treatment plan. This approach ensures better outcomes and a higher quality of life.
The Role of Global and National Health Policies in Diabetes Management
Global and national health policies play a pivotal role in shaping diabetes management strategies. These policies influence everything from treatment coverage to prevention programs, ensuring better outcomes for individuals worldwide. By addressing both medical and socioeconomic factors, they aim to reduce the burden of this chronic disease.
Insights from the Global Diabetes Compact and WHO Initiatives
The Global Diabetes Compact, launched by the World Health Organization, is a key initiative driving global health strategies. It focuses on improving access to care and medication, especially in low- to middle-income countries. The compact emphasizes early diagnosis and prevention, aiming to reduce complications like kidney damage and cardiovascular issues.
Recent resolutions from the World Health Assembly have further strengthened these efforts. They call for enhanced diabetes surveillance and better integration of diabetes care into national health systems. These guidelines are particularly crucial for regions with limited resources, where treatment coverage is often the lowest.
How U.S. Health Policies Can Shape Future Outcomes
In the U.S., national policies are instrumental in improving diabetes management. Programs like the National Diabetes Prevention Program focus on lifestyle changes to reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes. These initiatives are backed by evidence, showing that community-based interventions can prevent or delay the onset of the disease.
Policy changes, such as Medicare coverage for diabetes prevention programs, also play a significant role. By expanding access to care and medication, these policies help reduce disparities in health outcomes. They ensure that even underserved populations receive the support they need to manage their condition effectively.
“Effective health policies are the cornerstone of diabetes prevention and management, ensuring equitable access to care for all.”
Looking ahead, updated health policies will continue to shape the future of diabetes management. By focusing on prevention, early diagnosis, and equitable access to treatment, we can work towards a healthier future for everyone.
Conclusion
Diabetes continues to impact millions globally, with rising trends shaping healthcare priorities. Over the past decades, global diabetes rates have surged, driven by lifestyle changes and aging populations. Early detection and effective prevention strategies are crucial to reducing complications like blood vessel damage and kidney issues.
Understanding the differences between type 1 and type diabete is essential for proper management. While type 1 requires insulin, type 2 can often be managed with lifestyle changes and medication diabete. Both types demand proactive care to avoid long-term health risks.
Health policies play a vital role in addressing this challenge. Initiatives like the Global Diabetes Compact aim to improve access to care and prevention programs. By staying informed and taking action, every adult can contribute to better health outcomes.
FAQ
What is diabetes and how does it affect your body?
Diabetes is a chronic disease where your body struggles to manage blood sugar levels. It can damage blood vessels, kidneys, and other organs if not controlled. Early diagnosis and proper care are essential to prevent complications.
How does type 1 diabetes differ from type 2 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes occurs when your body doesn’t produce insulin, while type 2 diabetes happens when your body doesn’t use insulin effectively. Type 2 is more common and often linked to lifestyle factors like diet and physical activity.
What are the key symptoms of diabetes to watch for?
Common symptoms include frequent urination, excessive thirst, fatigue, and blurred vision. If you notice these signs, consult a healthcare professional for blood glucose testing.
How can you lower your risk of developing type 2 diabetes?
Maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, and staying physically active can significantly reduce your risk. Regular health screenings also help catch early signs.
What treatment options are available for diabetes?
Treatment includes medication, insulin therapy, and lifestyle changes. Managing blood sugar levels through diet, exercise, and regular monitoring is crucial for long-term health.
Why is diabetes treatment coverage lower in low- to middle-income countries?
Limited healthcare resources and infrastructure often result in lower treatment coverage. Global initiatives like the Global Diabetes Compact aim to address these disparities.
How do global diabetes trends compare to those in the US?
While the US faces high diabetes rates, low- to middle-income countries often experience faster growth due to lifestyle changes and limited access to care. Both regions need targeted prevention strategies.
What role do health policies play in diabetes management?
Policies like the Global Diabetes Compact and WHO initiatives promote better access to care and prevention programs. In the US, policies can shape outcomes by improving treatment and education.
What are the long-term complications of unmanaged diabetes?
Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to heart disease, kidney failure, vision loss, and nerve damage. Regular monitoring and treatment are vital to avoid these risks.
How does socioeconomic status impact diabetes prevalence?
Lower socioeconomic status often limits access to healthy food, healthcare, and education, increasing diabetes risk. Addressing these factors is key to reducing disparities.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Share this article:
Meet Gluco 6
Blood sugar balance supplement
Tired of Type-2 controlling your life or worried that persistent high blood sugar may turn into something worse? Then yes, Gluco6 is right for you.
Gluco6 has already provided amazing blood sugar assistance for men and women in their 30s, 40, 50s and even 80s. Because it was formulated based on cutting-edge science and groundbreaking ingredients, Gluco6 is engineered to rapidly assist even the most erratic blood sugar levels.